There is a rising awareness of the effects of toxic chemicals in our lives and it is making people act. Tellus Think Tank speaks with Madeleine Norman, one of the pioneers in the growing “Plastic diet” movement. Members of the plastic diet movement want to rid their lives of toxic chemicals and perform “plastic diets” in their homes. Read more…
Text: Domi, Tellus Think Tank Photo: Madeleine Norman & AnnVixen
Plastic diet – rid your life from toxins
In Tellus Think Tank’s last article we met Åsa Arrhenius, PhD in Ecotoxicologi at the University of Gothenburg. We learnt about the hundreds of thousands of chemicals in our lives and we are getting exposed to them through what we buy and bring home; food, clothing, furniture, body products and household chemicals. Chemical substances like PVC, Phthalates, Bisphenol A are either carcinogenic, affect human fertility or cause allergies.

Public awareness is still low, or latent, and most people still lack awareness of the effects of the chemicals overflowing their lives and homes.
A new movement is slowly dawning and some of the pioneers can be found in the Facebook group “Plastic diet” (the actual Swedish name on Facebook is “Plastbanta”) where members share ideas on how to reduce the amount of plastic in their homes. For English readers the equivalent groups are the “No Waste groups”.
Madeleine Norman is one of the active plastic dieters in the group and has soon plastic dieted her entire home. For Madeleine it all started with a lecture in Environmental Sciences at Linköping University, five years ago.
Pregnant and toxic living
Madeleine was pregnant during her studies in Environmental Science and attended a lecture on biology, chemistry and climate change. After the lecture, she broke down in sobs under the weight of her newly found knowledge about the toxins in

her everyday life. She was struck by an overwhelming worry of how the chemicals could be effecting her yet unborn child.
The lecture Madeleine attended had covered the subject of Bisphenol A’s effects on male fetuses. The chemical increases risk for male children to be born with damaged genital organs and can seriously affect men’s sperm production.
The realisation that this chemical and other harmful chemicals like PVC and Polyethylene Phthalates are to be found everywhere in our everyday lives became too much to bear and Madeleine began researching how she could adjust her life to contain less toxins.
Toxins everywhere
Madeleine’s quest started by finding out where the harmful chemicals, such as Polyethylene Phthalates, could be found. One unexpected place was in textile rainwear. The plastic in rain clothes has been hardened and normally doesn’t release plastic particles. However, when heated in a washing machine, the toxins are released into the water.
Modern water and waste treatment plants are not able to distinguish micro plastic particals from the water. In the first step the micro plastics are rinsed out into our lakes and seas. In the following steps of the ecosystem they are eaten by plankton, then fish, birds and humans. Madeleine says her University studies in Environmental Sciences taught the students about the increased amount of cancer found in fish.
The start of the Plastic diet

Madeleine began with her plastic diet and says that she originally wanted to throw out all the plastic in her life. She and her man where just in the beginning of creating a home so they replaced all the plastic things that they could afford.
– “We googled everything. The bedroom was most difficult with the foam mattress and polyester quilts. Down comforters are a good alternative. We bought an organic mattress filled with a mixture of coconut and cotton from Green Interior. Jysk has pillows with cotton filling”, says Madeleine and continues, “for toddlers one can find mattresses stuffed with buckwheat shells. Friends of mine ordered Japanese futons stuffed with cotton. All options are relatively expensive compared with IKEA. ”
Madeleine shares insights from a survey performed by the Swedish Emergency Services which showed that IKEA furniture, during a fire, emits both formaldehyde and water toxins. She continues to tell me that she thinks IKEA does mostly good things in sustainability and highlights a good example where IKEA is offering a whole collection made of cork.
-It is good when large companies are motivated to increase sustainability, she says, because it affects so many!
Toxins in body care products

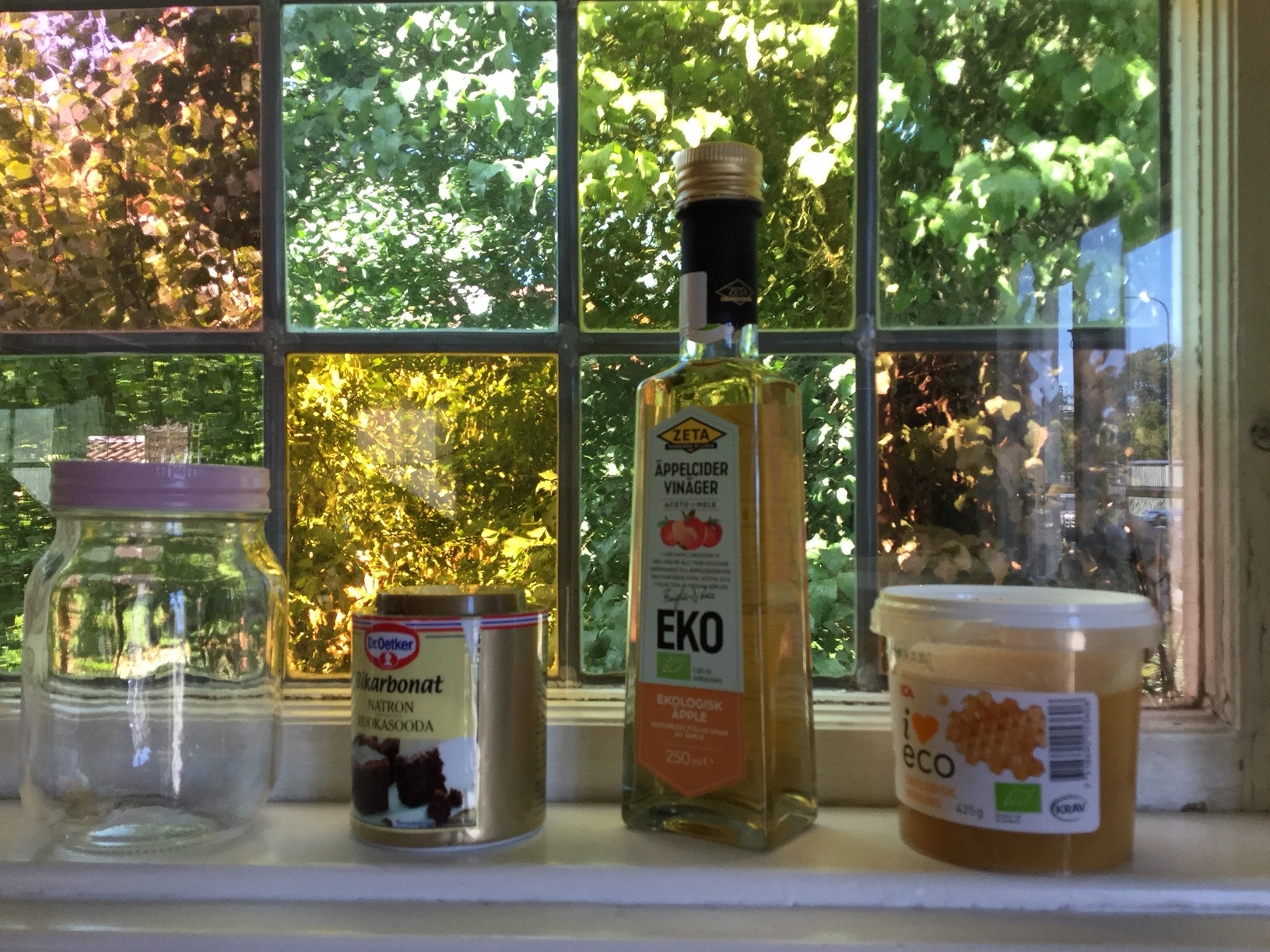
Another hurdle that Madeleine found was difficult to overcome were toxins found in various body care products. Nowadays she only uses “No’poo” products.
(“No’Poo” is a non-toxic movement, the name shows the combined struggle of “Not using shampoo” and reducing chemical crap in one’s life.) She often washes her hair in home-made mixtures of eggs, honey and baking soda (see Madeleines recipes). Madeleine also mentions organic shampoo cakes from LUSH. More on Madeleines homemade shampoo here…
Toxins in food and food packaging

Grocery shopping often means bringing home an array of toxic plastic. Supermarkets often pack their foods in plastics containing Bisphenol A and almost all vegetables are placed in thin plastic bags to ease weighing and transportation. Paper bags are seldom available as an alternative.
Madeleine washes her fruits and vegetables as soon as she arrives home and keeps them in glass or metal containers. The downside with this practise is that the food doesn’t last as long as in plastic but that is a trade-off that she is willing to make. Madeleine prolongs the life of her cucumbers by storing them in a stainless steel container with a lid. In the summer she grows her own cucumber on the balcony, to avoid the plastic packed cucumber from the supermarkets.
Madeleine’s home and advice for people who want do their own “plastic diet”
Madeleine shares some advice to those who are interested in doing their own plastic diet. She recommends to start ones plastic diet the kitchen. She especially recommends changing out plastic wear that is heated – as this is when plastics emit particles and toxins. The first thing she recommends to remove are the pans with Teflon, plastic spatulas and the like.
-Buy Cast iron boilers or boilers in stainless steel or carbon steel. Ikea has sustainable alternatives. Replace your plastic water kettle with one made in stainless steel, says Madeleine.
She shares advice on cooking in the microwave oven. Many people heat their food in plastic containers. It is better to put the food on a china plate and to stop using the plastic splash guard all together.
In Madeleine’s home there are no plastic toys to be found. They use a lot of porcelain and glass. Food is stored in steel, glass and porcelain. We learn that her linoleum floors don’t contain plastic when looking this up in the book “Rumsrent”. According to this book linoleum contains linseed oil, rosin, wood flour or cork flour.
Much of Madeleines furniture is made of solid wood and has been purchased at flea markets. She guesses that the wood might have been lacquered with epoxy varnish, often containing Bisphenol. If a piece of furniture has been varnished Madeleine won’t remove it as the dry coat of varnish doesn’t release particles. However if she needs to treat a piece of furniture, she would rather use linseed oil than paint or varnish.
Plastics difficult to replace?

Madeleine says that it has been difficult for her to replace the foam mattress of her bed and they have still not been able to afford to do so.
It is certainly difficult to live without plastic altogether and Madeleine takes up the world of health care. Plastic tubes containing Bisphenol A are used for feeding premature infants, as the chemical soften the plastic probe. So far there are no alternatives to the Bisphenol softened plastic probes but Madeleine finds their use preferable as they make it possible to save the lives of infant children.
Madeleine reveals that she underwent surgery at age seven and was given a plastic implant. She reasons that if the plastic implant gives her cancer at the age of 50, it has nonetheless given her 40 years extra to live. Sometimes it is very easy to choose the plastic option.
Innovative plastic dieters impress
Socially Madeleine moves in circles where knowledge of the effect of plastic is high and several persons have done the plastic diet treatment on their homes. She guesses that the general public is less knowledgeable about the over-exposure to toxic substances from plastics and other stuff in our lives.
We discuss the “Plastic Diet”- and Zero Waste groups – on Facebook and Madeleine says that she is impressed and fascinated by how innovative people are. Some avoid paper handkerchiefs if in plastic packaging. Others buy their food in bulk to avoid plastic wrapped food (this is hardly possible in Sweden). There are also individuals that crochet their own cloths in linen to avoid micro fiber cloths.
How do you think Sweden should adapt its legislation on plastic?
-Sweden has a well developed system for waste collection, says Madeleine.
She still has a couple of improvements to suggest, such as that the public waste collection stations also should be open to more plastics than just plastic packaging. She is sure that this would give some quick improvements.
Most countries could stop plastic at its source by banning disposable plastic items like bags and packaging. (See article on Rwanda’s plastic ban)

A plastic ban of this kind would bring significant savings to municipalities. It would save costs from having to gather plastic garbage from streets. The large amount of plastics having to be handled in waste plants would be reduced. A plastic ban would also bring better public health.
What advice, in addition to the above, you want to give to people just starting off with their plastic diet?
-Don’t panic. I tried that when starting out with my plastic diet and it made me feel pretty bad. My advice is to use the plastic stuff that you have at home until it’s not fit for its purpose anymore. Make the better, plastic free choice next time. Change takes time! Smiles Madeleine Norman.
In Tellus Think Tank’s next article we meet Fäviken that has been awarded two Guide Michelin stars. The Fäviken food policy strives to serve locally produced food. Tellus Think Tank will sort out if that works when being located in the Northern wilderness of Sweden get notified when the article is available!